Continuous Aggregates (TimescaleDB)
Continuous aggregates는 MATERIALIZED VIEW를 사용하여 정의된 쿼리를 미리 실행하고, 그 결과를 물리적으로 저장해 둡니다. 이를 통해 대용량 데이터의 집계 쿼리를 더 빠르게 조회할 수 있습니다.
예제
-- 1시간 단위 집계 Continuous Aggregate 생성
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW one_hour_transactions
WITH (timescaledb.continuous) AS
SELECT
time_bucket('1 hour', time) AS bucket,
count(*) AS tx_count,
sum(fee) AS total_fee_sat,
sum(fee_usd) AS total_fee_usd,
stats_agg(fee) AS stats_fee_sat,
avg(size) AS avg_tx_size,
avg(weight) AS avg_tx_weight,
count(
CASE
WHEN (fee > output_total) THEN hash
ELSE NULL
END
) AS high_fee_count
FROM transactions
WHERE (is_coinbase IS NOT TRUE)
GROUP BY bucket;
-- 리프레시 정책 설정 (3일 전 ~ 1일 전까지, 하루 단위 실행)
SELECT add_continuous_aggregate_policy('one_hour_transactions',
start_offset => INTERVAL '3 days',
end_offset => INTERVAL '1 day',
schedule_interval => INTERVAL '1 day');
💡 핵심 개념
- MATERIALIZED VIEW — 정의된 쿼리를 미리 실행하여 물리적으로 저장. 반복 조회 시 매우 빠름.
timescaledb.continuous— TimescaleDB에 Continuous Aggregates 사용을 지정하는 옵션.time_bucket()— 일정한 간격(예: 1시간, 1일)으로 시간을 버킷 단위로 묶어 집계하는 함수.
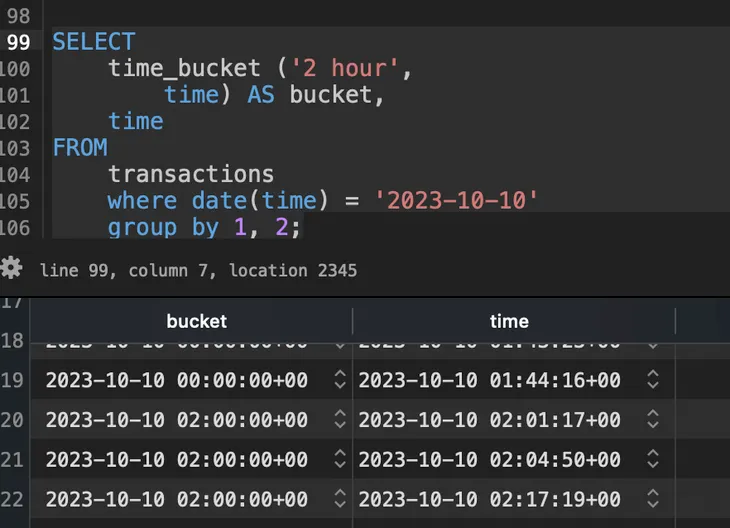
time_bucket() 예시
TIP: 리프레시 정책(start/end offsets)을 적절히 설정하면 최신 데이터 반영 속도와 저장소 사용량을 균형 있게 조절할 수 있습니다.
'데이터 엔지니어링 > DB' 카테고리의 다른 글
| DB 및 grafana 생성 및 데이터 마이그레이션 (0) | 2025.08.10 |
|---|---|
| TimescaleDB special function? 먼데? (6) | 2025.08.10 |
| Postgres DB는 이렇게 생겼다! (0) | 2025.08.10 |


